Teaching customer relationship management (CRM)

In a world where big data and business analytics make the headlines daily, it is useful to remind students that 90% of data collected by companies is indeed marketing data. Customer relationship management (CRM) is an approach to optimize a company’s interactions with its current and prospective customers. It extensively uses data analysis about customers’ history with a company to improve business operations, specifically focusing on customer retention and sales growth. The Enginius models best suited for a CRM course are therefore those relying on sales or behavioral data tracked and stored in companies’ customer databases.
If you are teaching customer relationship management these are the Enginius models and case studies we recommend for you…
Not familiar with Enginius yet? Click here to discover how Enginus can boost your teaching.
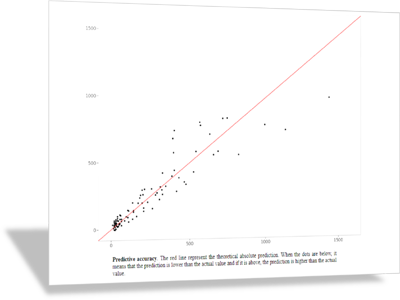
Predictive modeling
The predictive module in Enginius is a powerful and versatile regression model that helps managers predict a variety of outcomes, such as loyalty, brand choice, response to an offer, expected revenues, or click-through rate, based on a set of available predictors in the customer database. Most customer databases contain a treasure trove of data to perform predictive analytics, so covering this in a customer relationship management course should be a no-brainer. One of the most appropriate case studies for your course is the Hope Foundation (predictive modeling) case study, where a charity uses past donation data to identify their most promising contacts in their donor database.
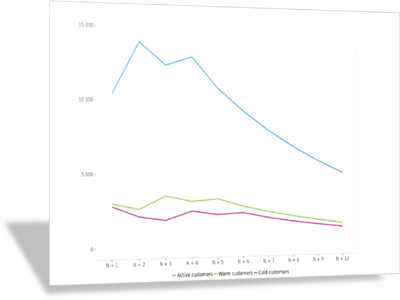
Customer lifetime value
Looking at how customers transition from one segment to another over time, and how each segment is valued to the company, it is possible to estimate the expected value of a customer over its entire lifetime, and allocate company resources accordingly. Case studies like SyPhone or Northern Aero drive these points home.
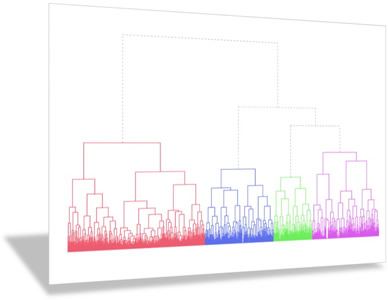
Segmentation
In the magma of a customer database, customers are described by so many variables, it is often hard to make sense of them. Segmentation analysis helps a company group customers into clusters based on their similarities, and therefore identify behavioral patterns.




